🧩 Introduction: Why PDFs Rule the Digital World
From student assignments to business reports, academic journals to eBooks—PDFs are everywhere. You’ve probably downloaded or shared hundreds of them without thinking twice. But have you ever paused to ask: What does PDF stand for? Why is this format so widely used across Education, industry, publishing, and even governments?
In this in-depth blog, we break down what does PDF stand for, its origins, who created it, how it’s used today, its file structure, history, benefits, and its ongoing relevance in the 21st century. Whether you’re a student, an educator, a professional, or just a curious digital citizen, you’ll find this post packed with actionable insights, historical trivia, and real-world applications.

Table of Contents
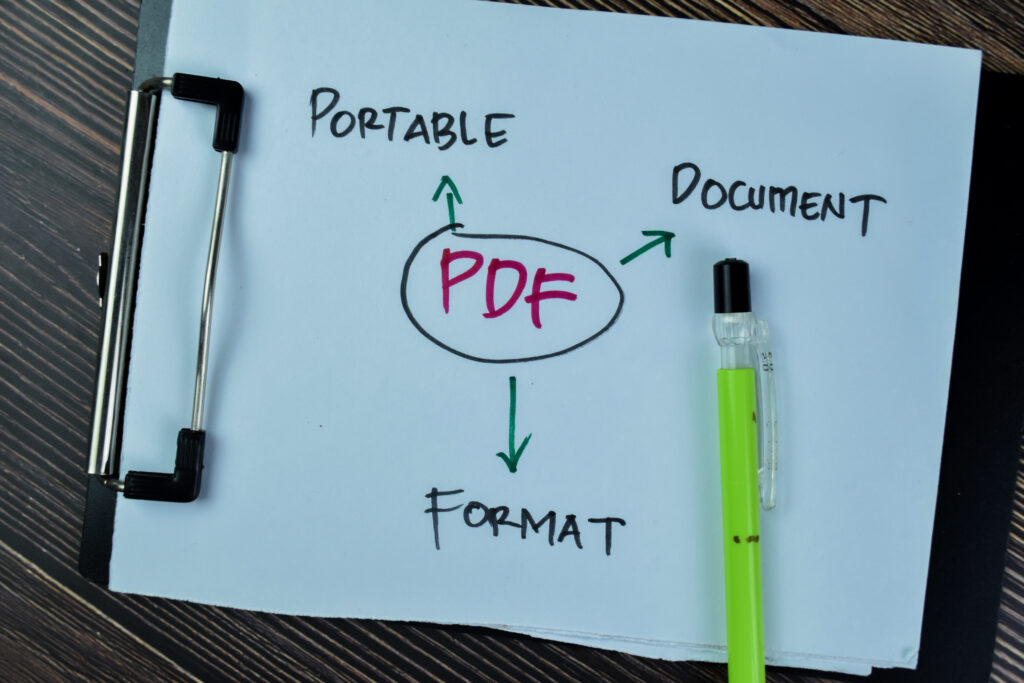
1. 🔤 What Does PDF Stand For?
PDF stands for “Portable Document Format.”
It’s a file format developed by Adobe in the early 1990s to allow documents to be presented and shared consistently, regardless of the software, hardware, or operating system used to create or view them.
A PDF file encapsulates a complete document with:
- Text
- Fonts
- Images
- Graphics
- Hyperlinks
- Interactive elements (forms, checkboxes, etc.)
This makes it universally compatible, which is why students, teachers, businesses, legal professionals, and governments rely on PDFs for long-term document sharing and collaboration.
2. 👨🔬 Who Invented PDF and Why?
PDF was created by Adobe Systems in 1991 as part of a project called “Camelot”, initiated by Adobe co-founder Dr. John Warnock.
🔗 Source: Adobe Blog on the 25th Anniversary of PDF
🧠 Purpose of PDF Creation:
At that time, sharing documents across different systems (Mac, Windows, Unix) was a nightmare. Fonts would break, layouts would shift, and formatting would get corrupted.
Warnock’s vision was simple but revolutionary:
“Imagine if you could send a document from one computer to another and have it print exactly the same everywhere.”
Thus, PDF was born to solve one critical problem: document integrity.

3. 📈 The Evolution of the PDF Format
1993: The PDF 1.0 Specification
PDF was first released to the public in 1993, but adoption was slow due to:
- Large file sizes
- No support in browsers
- Proprietary nature
Late 1990s–2000s: Adobe Acrobat Expansion
PDF gained traction with the release of Adobe Acrobat, and tools like Distiller and Reader became standard in offices and schools.
2008: PDF Becomes an Open Standard
Adobe handed over PDF to the International Organisation for Standardisation (ISO) in 2008.
- Now officially known as ISO 32000.
- PDF is no longer proprietary.
🔗 Source: ISO 32000-1:2008
4. 🆚 What Makes PDF Different from Other Formats?
Let’s compare PDF with other formats:
FormatStrengthsWeaknesses
PDF preserves layout, is cross-platform, secure, and Less editable
DOCX is Easy to edit. Format may shift
TXT Lightweight No formatting
HTML is Great for the web, not ideal for printing
JPG Good for images, not suitable for documents
PDF is the perfect mix of visual integrity, interactivity, and portability.
5. 🧬 Anatomy of a PDF File
A PDF file consists of four main components:
- Header: Declares the PDF version
- Body: Contains objects like text, images, and fonts
- Cross-reference Table (xref): Keeps track of all objects
- Trailer: Tells the PDF reader where to find the xref and root object
Each element is carefully indexed to allow quick loading, scrolling, and rendering.
6. 🎓 Common Uses of PDF in Education and Business
📘 In Education:
- Assignment submissions
- Scanned handwritten notes
- Digital textbooks
- Research papers
- Portfolio creation
💼 In Business:
- Contracts and legal documents
- HR onboarding forms
- Annual reports
- Product manuals
- Invoices
PDFs are often signed digitally and stored securely for long-term use.
🔗 Example Tool: DocuSign
7. 🔄 PDF File Variants: What Do They Mean?
There are several specialised types of PDF files used in specific industries:
Type Use Case
PDF/A Long-term archiving (used by libraries, institutions)
PDF/X Professional printing and publishing
PDF/E Engineering documentation
PDF/UA Accessible PDFs for screen readers
PDF/VT Variable and transactional printing
8. 🛠️ Tools to Create, Edit, and Convert PDFs
💻 Desktop Tools:
🌐 Online Tools:
- PDFEditingBuddy.com — Student-friendly free tools for converting, merging, compressing, protecting, and unlocking.
- ILovePDF
- Smallpdf
- Sejda PDF
🔁 Conversion Examples:
💡 Need a reliable student tool? Try PDFEditingBuddy.
9. 📱 Accessibility and Mobile Use of PDFs
Thanks to cloud syncing and mobile optimisation, PDFs are now accessible on the go.
Mobile Apps:
- Adobe Acrobat Reader Mobile
- CamScanner
- Xodo PDF
- Google Drive PDF Viewer
PDFs on mobile allow:
- Signing documents with a finger
- Filling forms directly
- Highlighting and annotating for study
- Reading eBooks and academic papers
PDF Accessibility:
Accessible PDFs are built with tags, alternate texts, and logical structures to support:
- Screen readers
- Text-to-speech engines
- Navigation for visually impaired users
🔗 Resource: WebAIM PDF Accessibility Guide
10. ☁️ The Future of PDFs in a Cloud-Based World
PDFs continue to evolve to meet the demands of:
- Remote learning
- Cloud collaboration
- eSigning and authentication
- Real-time annotation
Emerging features:
- Cloud-based PDF editing
- Blockchain-powered digital signatures
- AI-generated PDFs with interactive elements
With tools like PDFEditingBuddy, students and academics can now:
- Upload PNGs or DOCX
- Convert and merge files
- Compress and share PDFs—all within seconds, for free

11. ❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What does PDF stand for?
A: Portable Document Format
Q: Who created PDF, and when was it made?
A: Adobe Systems was led by John Warnock in 1993.
Q: Is PDF still relevant in 2025?
A: Absolutely. It remains the most universal and secure format for documents.
Q: Are PDFs editable?
A: Yes, with tools like Adobe Acrobat, PDF Editing Buddy, and others.
Q: What’s the difference between PDF and PDF/A?
A: PDF/A is designed for archiving and turns off certain features to ensure long-term preservation.
12. 🧠 Final Thoughts & Actionable Recommendations
PDF has come a long way from being just a “static document format.” It is now a powerful, versatile tool used in every industry, academic field, and digital process. Understanding what PDF stands for, how it works, and why it was invented not only enhances your digital literacy—it empowers you to use it more effectively.
✅ Summary Checklist:
- What does PDF stand for? = Portable Document Format
- Created by Adobe to solve document consistency problems
- Now an ISO open standard
- Used across Education, Business, legal, and technical fields
- Compatible with all devices
- Supports accessibility, security, and interactivity
- Still evolving in a cloud-first world
Whether you’re submitting an assignment or signing a contract, PDFs ensure your document is viewed exactly as intended.
🚀 Call to Action
Looking for powerful, free, and fast PDF tools tailored for students and academics?
👉 Visit PDFEditingBuddy.com now
Convert images to PDFs, compress large files, merge multiple PDFs, and more—all without creating an account.
Make your documents brighter, cleaner, and easier to share!




